Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
From the information given, by applying Kepler's 3rd law,
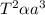
where;
T = period
a = semi major axis
T = 356 days (for earth)
a = 1 AU = 1.496
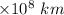
Therefore,
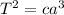
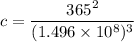
c = 3.9791
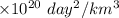
However, if the body in the solar system has a period of 10.759.22 days, then, a =?
∴
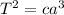
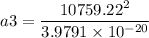
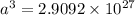
![a= \sqrt[3]{2.9092 * 10^(27)}](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/business/high-school/h3092ljiu3y81rpwizm51xf91ad0ve21ea.png)
a = 1.4275
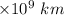
However, the velocity for a perihelion = 10.18 km/s
Using the formula
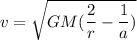 to calculate the radius, we have:
to calculate the radius, we have:
G =

M =
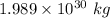
r = perihelion
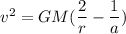
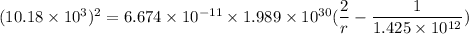
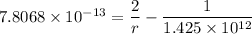
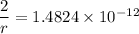
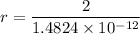
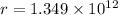
Similarly, the perihelion is expressed by the equation,
r = a(1 - e)
where ;
e= eccentricity
∴
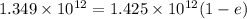
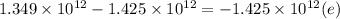
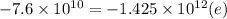
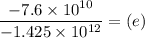
e ( eccentricity) = 0.0533
Aphelion radius in natural miles, r = a( 1+ e)
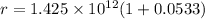
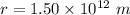
to nautical miles, we have:
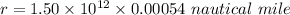
radius of aphelion
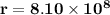 nautical miles
nautical miles
In respect to the value of a( i.e
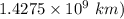
the body of the solar system is Saturn