
Given triangle is a right angled traingle
★ What does a right angle traingle have?
➢Hypotenuse(H)=The side of a right triangle opposite the right angle.
➢Perpendicular (P) = Exactly upright; extending in a straight line
➢Base(B)
➢ one angle is of 90⁰
➢Base and perpendicular are also known as leg of right angle traingle.
To solve such types of ques we use the theorem name "Pythagorean theorem"
which states that the square of the length of the hypotenuse of a right triangle is equal to the sum of the squares of those of the two other sides.
Now in mathematical way it can be written as :-
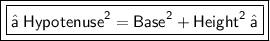

- Now let Base (p)be 6
- Perpendicular (q) be 2
- and hypotenuse be x
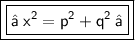

➢ Let's substitute the value
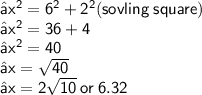

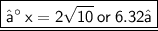
Hope it helps !