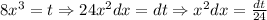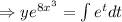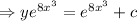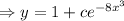Answer:
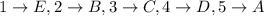
Explanation:
1.
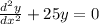
The characteristic equation for the given differential equation is:
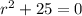
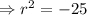
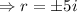
Since the roots are complex
Now, the general solution is:
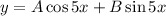
2.
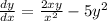
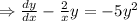
Divide both sides by
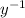
Let,
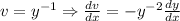
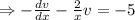
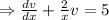
Here,
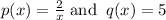
I.F.
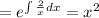
Now, the general solution is:
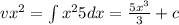
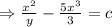
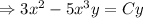
3.
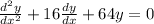
The characteristic equation is:
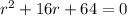
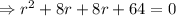
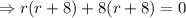
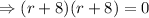
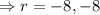
Since the roots are real and repeated.
Now, the general solution is:
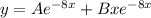
4.
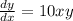
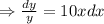
Integrating both sides
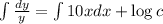
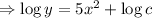
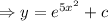
5.
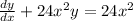
Here,
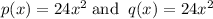
I.F.
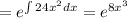
Now, the general solution is:
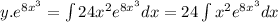
Let,