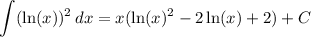Answer:
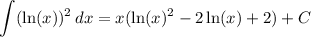
Explanation:
We want to evaluate the integral:
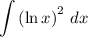
We can use Integration by Parts. Rewriting the integral yields:
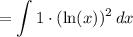
Recall that IBP is given by:
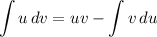
Let u be (ln(x))². And let dv be (1) dx. Therefore:
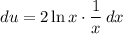
Simplify:
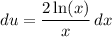
And:
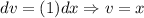
Therefore:
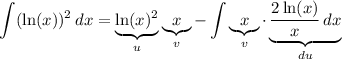
Simplify:
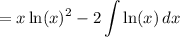
We can perform IBP again. Let u = ln(x) and v = 1. Hence:
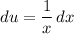
And:
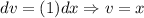
Thus:
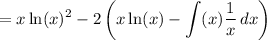
Simplify:
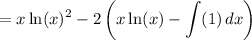
Evaluate:
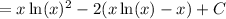
Simplify:
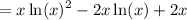
Factor:
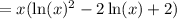
Therefore: