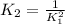The question is missing parts. The complete question is as follows.
Consider the two gaseous equilibria involving SO2 and the corresponding equilibrium constants at 298K:
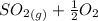 ⇔
⇔
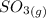 ;
;
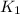
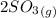 ⇔
⇔
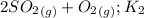
The values of the equilibrium constants are related by:
a)
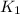 =
=
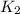
b)
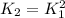
c)
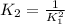
d)
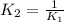
Answer: c)
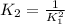
Explanation: Equilibrium constant is a value in which the rate of the reaction going towards the right is the same rate as the reaction going towards the left. It is represented by letter K and is calculated as:
![K=([products]^(n))/([reagents]^(m))](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/p59zfwqlaqhyiikwgtunjk3svv2l4xwnj3.png)
The concentration of each product divided by the concentration of each reagent. The indices, m and n, represent the coefficient of each product and each reagent.
The equilibrium constants of each reaction are:
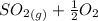 ⇔
⇔
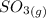
![K_(1)=([SO_(3)])/([SO_(2)][O_(2)]^(1/2))](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/41aria0h68yyomdc4ni9irqj4x5vauqimw.png)
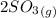 ⇔
⇔
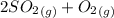
![K_(2)=([SO_(2)]^(2)[O_(2)])/([SO_(3)]^(2))](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/yq5ojlrqnzyimoiiixqvckmmjnibwquok6.png)
Now, analysing each constant, it is easy to see that
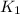 is the inverse of
is the inverse of
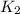 .
.
If you doubled the first reaction, it will have the same coefficients of the second reaction. Since coefficients are "transformed" in power for the constant, the relationship is: