Answer:
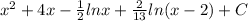
Explanation:
Given the integrand
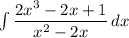 , before evaluating the integral function, we will need to simplify the function first by applying long division as shown in the attachment.
, before evaluating the integral function, we will need to simplify the function first by applying long division as shown in the attachment.
Hence the partial form of the function
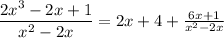
Integrating its partial sum
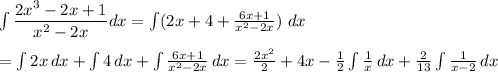
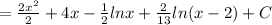
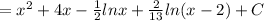
NB: Find the partial sum calculation also in the attachment.