Answer:
The null hypothesis gets rejected for the p-value of 0.04 and 0.042.
Explanation:
We are given the level of significance of
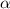 = 0.01 or 1%. And also we are provided with the different p-values.
= 0.01 or 1%. And also we are provided with the different p-values.
As we know that; the decision rule for rejecting the null hypothesis is given by;
- If the P-value of our test statistics is less than the level of significance, then we have sufficient evidence to reject our null hypothesis.
- If the P-value of our test statistics is more than the level of significance, then we have insufficient evidence to reject our null hypothesis.
(i) The P-value given is 0.002.
Here, the P-value is less than the level of significance as 0.002 < 0.01, then we have sufficient evidence to reject our null hypothesis. So, the null hypothesis gets rejected.
(ii) The P-value given is 0.009.
Here, the P-value is less than the level of significance as 0.009 < 0.01, then we have sufficient evidence to reject our null hypothesis. So, the null hypothesis gets rejected.
(iii) The P-value given is 0.04.
Here, the P-value is more than the level of significance as 0.04 > 0.01, then we have insufficient evidence to reject our null hypothesis. So, the null hypothesis does not get rejected.
(iv) The P-value given is 0.042.
Here, the P-value is more than the level of significance as 0.042 > 0.01, then we have insufficient evidence to reject our null hypothesis. So, the null hypothesis does not get rejected.