Answer: (-∞,-1) ∪ (0,+∞)
Step-by-step explanation: The representation fog(x) is a representation of composite function, meaning one depends on the other.
In this case, fog(x) means:
fog(x) = f(g(x))
fog(x) =
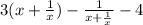
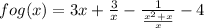
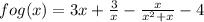
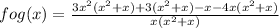
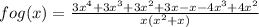
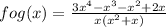
This is the function fog(x).
The domain of a function is all the values the independent variable can assume.
For fog(x), denominator can be zero, so:
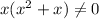
If x = 0, the function doesn't exist.
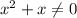
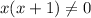
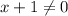
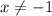
Therefore, the domain of this function is: -∞ < -1 or x > 0