Answer: ΔH°f of gaseous nitrogen monoxide is 148.0 kJ/mol
Step-by-step explanation:
The balanced chemical reaction is,
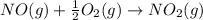
The expression for enthalpy change is,
![\Delta H_(rxn)=\sum [n* \Delta H_f(product)]-\sum [n* \Delta H_f(reactant)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/hqnuyuykr2frm6qyk5sivyqflgpkxwvp3u.png)
![\Delta H_(rxn)=[(n_(NO_2)* \Delta H_f_(NO_2))]-[(n_(O_2)* \Delta H_f_(O_2))+(n_(NO)* \Delta H_f_(NO))]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/gsfv93wq3emvqowadrl2t3fl5gclnn65o2.png)
where,
n = number of moles
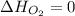 (as heat of formation of substances in their standard state is zero
(as heat of formation of substances in their standard state is zero
Now put all the given values in this expression, we get
![-114.14=[(1* 33.90)]-[((1)/(2)* 0)+(1* \Delta H_f{NO})]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/cbdvhwb5dod4o1xyoau397272z9809ruci.png)
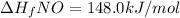
Therefore, ΔH°f of gaseous nitrogen monoxide is 148.0 kJ/mol