Answer:
Kc for this equilibrium is 2.30*10⁻⁶
Step-by-step explanation:
Equilibrium occurs when the rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the reverse reaction and the concentrations of reactants and products are held constant.
Being:
aA + bB ⇔ cC + dD
the equilibrium constant Kc is defined as:
![Kc=([C]^(c)*[D]^(d) )/([A]^(a) *[B]^(b) )](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/85hwm7oyfepdmpzx43xau1gchg0a7czs9h.png)
In other words, the constant Kc is equal to the multiplication of the concentrations of the products raised to their stoichiometric coefficients by the multiplication of the concentrations of the reactants also raised to their stoichiometric coefficients. Kc is constant for a given temperature, that is to say that as the reaction temperature varies, its value varies.
In this case, being:
2 NH₃(g) ⇔ N₂(g) + 3 H₂(g)
the equilibrium constant Kc is:
![Kc=([N_(2) ]*[H_(2) ]^(3) )/([NH_(3) ]^(2) )](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/29vyqsox053h4ipvu7jk2s5qbf72bno6bf.png)
Being:
- [N₂]= 0.0551 M
- [H₂]= 0.0183 M
- [NH₃]= 0.383 M
and replacing:
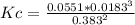
you get:
Kc= 2.30*10⁻⁶
Kc for this equilibrium is 2.30*10⁻⁶