Answer:
The p-value of the test is 0.049.
Explanation:
The dependent t-test (also known as the paired t-test or paired samples t-test) compares the two means associated groups to conclude if there is a statistically significant difference amid these two means.
In this case a paired t-test is used to determine whether the experimental toothbrush was effective or not.
The hypothesis for the test can be defined as follows:
H₀: The experimental toothbrush was not effective, i.e. d = 0.
Hₐ: The experimental toothbrush was effective, i.e. d < 0.
The information provided is:
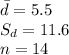
Compute the test statistic value as follows:
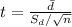
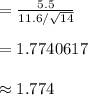
The test statistic value is 1.774.
Decision rule:
If the p-value of the test is less than the significance level then the null hypothesis will be rejected and vice-versa.
Compute the p-value of the test as follows:
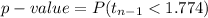
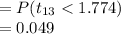
*Use a t-table.
The p-value of the test is 0.049.
p-value= 0.049 > α = 0.05
The null hypothesis will be rejected.
Thus, it can be concluded that experimental toothbrush was effective.