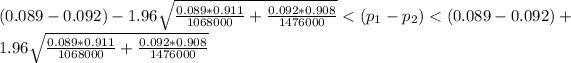Complete Question
The complete question is shown on the first uploaded image
Answer:
The interval is

Explanation:
From the question we are told that
The first sample size is
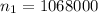
The first sample proportion is
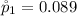
The second sample size is
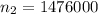
The second sample proportion is
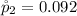
Given that the confidence level is 95% then the level of significance is mathematically evaluated as
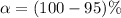
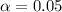
Next we obtain the critical value of
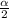 from the normal distribution table
from the normal distribution table
The value is
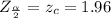
Generally the 95% confidence interval is mathematically represented as
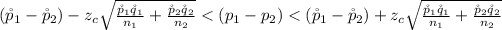
Here
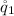 is mathematically evaluated as
is mathematically evaluated as
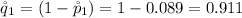
and
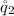 is mathematically evaluated as
is mathematically evaluated as
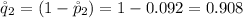
So