Answer:
The final pressure is 1556 mmHg
Step-by-step explanation:
The gas laws are a set of chemical and physical laws that allow determining the behavior of gases in a closed system.
Boyle's law says that "The volume occupied by a given gaseous mass at constant temperature is inversely proportional to pressure" and is expressed mathematically as: P * V = k
Charles's law states that the volume of gas at constant pressure is directly proportional to its temperature and is expressed mathematically as the quotient that exists between the volume and the temperature equal to a constant value:
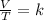
Gay - Lussac's law states that the pressure of gas at constant volume is directly proportional to its temperature and is expressed mathematically as the quotient between pressure and temperature equal to a constant:
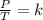
Combined law equation is the combination of three gas laws called Boyle's, Charlie's and Gay-Lusac's law:
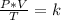
When you want to study two different states, an initial one and a final one of a gas, it is possible to apply:
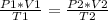
In this case:
- P1= 570 mmHg
- V1= 2270 mL
- T1= 25 C= 298 K (being 0 C= 273 K)
- P2= ?
- V2= 1250 mL
- T2= 175 C=448 K
Replacing:
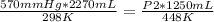
Solving:
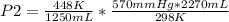
P2= 1556 mmHg
The final pressure is 1556 mmHg