Answer:
There is sufficient evidence to conclude that the new algorithm has a lower mean completion time than the current algorithm
Explanation:
From the question we are told that
The sample size for each algorithm is
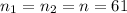
The sample mean for new algorithm is
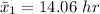
The standard deviation for new algorithm is
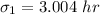
The sample mean for the current algorithm is
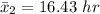
The standard deviation for current algorithm is
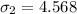
The level of significance is
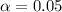
The null hypothesis is
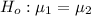
The alternative hypothesis is
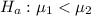
Here
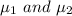 are population mean for new and current algorithm
are population mean for new and current algorithm
Generally the test statistics is mathematically represented as
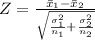
=>
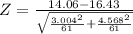
=>

Generally the p-value is mathematically represented as
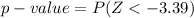
From the z-table
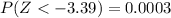
=>
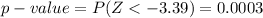
From the calculated value we see that
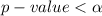 hence the null hypothesis is rejected
hence the null hypothesis is rejected
Hence we can conclude that there is sufficient evidence to conclude that the new algorithm has a lower mean completion time than the current algorithm