Answer:
a) t = 59 s , b) t = 107 s , c) t = 466 s
Step-by-step explanation:
This is an exercise in thermal conductivity. The power dissipated or transferred is
P = Q / Δt = k A dT/dx
where Q is the thermal energy of the bar, k the constant of thermal conductivity.
If we assume that we are in a stable regime
dT / dx = (T₀ -
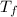 ) / L
) / L
the energy in the bar is
Q = m
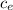 T₀
T₀
we substitute
m c_{e} T₀ / t = k A (T₀ -T_{f}) / L
t = c_{e} / k m L / A T₀ / (T₀ -T_{f})
let's use the concept of density
ρ = m / V
V = A L
m = ρ AL
t = c_{e} / k (ρ A L) L / A T₀ / (T₀ -T_{f})
t =
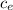 /k ρ L² T₀/(T₀ -T_{f})
/k ρ L² T₀/(T₀ -T_{f})
In this exercise, the initial temperature is T₀ = 100ºC, the final temperature is T_{f }= 5ºC and the length
L = L₀ / 2 = 20/2 = 10cm = 0.1m
a) case of silver
c_{e} = 234 J / kg ºC
k = 437 W / m ºC
ρ = 10,490 10³ kg / m³
let's calculate
t = 234/437 10.49 10³ 0.1² 100 / (100 -5)
t = 59 s
b) case materials aluminum
c_{e} = 900 J / kg ºC
k = 238 W / m ºC
ρ = 2.70 10³ kg / m³
t = 900/238 2.70 10³ 0.1² 100 / (100-5)
t = 107 s
c) iron material
c_{e} = 448 J / kg ºC
k = 79.5 W / m ºC
ρ = 7.86 10³ kg / m³
t = 448 / 79.5 7.86 10³ 0.1² 100 / (100-5)
t = 466 s