Answer:
The greater of the two currents is 0.692 A
Step-by-step explanation:
Given;
distance between the two parallel wires; r = 6 mm = 6 x 10⁻³ m
let the current in the first wire = I₁
then, the current in the second wire = 2I₁
length of the wires, L = 3.0 m
magnitude of force on the wires, F = 8 μN = 8 x 10⁻⁶ N
The magnitude of force on the two parallel wires is given by;
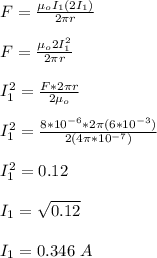
the current in the second wire = 2I₁ = 2 x 0.346 A = 0.692 A
Therefore, the greater of the two currents is 0.692 A