Answer:
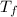 = -29.96 °C
= -29.96 °C
Explanation: A solution has a lower freezing point compared to the pure solvent, due to the solute lowering the vapor pressure of the solvent.
The "new" freezing point is calculated as:
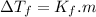
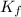 is the molal freezing-point depression constant
is the molal freezing-point depression constant
m is molality concentration, i.e., moles of solute per kilogram of solvent
Before calculating freezing point, let's find moles of ethylene glycol (
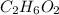 ) in the solution:
) in the solution:
Molar mass
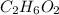 = 62.08 g/mol
= 62.08 g/mol
For 500 g:
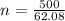
n = 8.05 moles
The molality concentration for 0.5kg of water:
m =
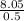
m = 16.11
The freezing point will be:
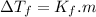
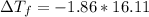
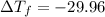
Freezing point of a solution of Ethylene Glycol and Water is -29.96°C