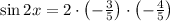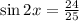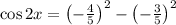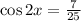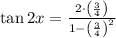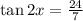Answer:
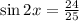 ,
,
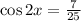 ,
,
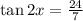
Explanation:
The sine, cosine and tangent of a double angle are given by the following trigonometric identities:
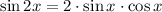
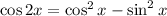
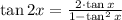
According to the definition of sine function, the ratio is represented by:
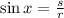
Where:
 - Opposite leg, dimensionless.
- Opposite leg, dimensionless.
 - Hypotenuse, dimensionless.
- Hypotenuse, dimensionless.
Since
 , measured in sexagesimal degrees, is in third quadrant, the following relation is known:
, measured in sexagesimal degrees, is in third quadrant, the following relation is known:
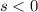 and
and
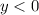 .
.
Where
 is represented by the Pythagorean identity:
is represented by the Pythagorean identity:
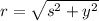
The magnitude of
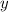 is found by means the Pythagorean expression:
is found by means the Pythagorean expression:
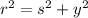
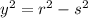
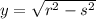
Where
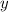 is the adjacent leg, dimensionless.
is the adjacent leg, dimensionless.
If
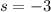 and
and
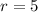 , the value of
, the value of
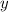 is:
is:
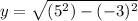
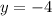
Then, the definitions for cosine and tangent of x are, respectively:
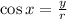
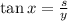
If
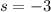 ,
,
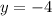 and
and
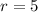 , the values for each identity are, respectively:
, the values for each identity are, respectively:
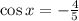 and
and
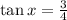 .
.
Now, the value for each double angle identity are obtained below: