Answer:
The water is flowing at the rate of 28.04 m/s.
Step-by-step explanation:
Given;
Height of sea water, z₁ = 10.5 m
gauge pressure,
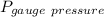 = 2.95 atm
= 2.95 atm
Atmospheric pressure,
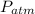 = 101325 Pa
= 101325 Pa
To determine the speed of the water, apply Bernoulli's equation;
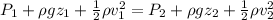
where;
P₁ =
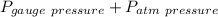
P₂ =
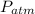
v₁ = 0
z₂ = 0
Substitute in these values and the Bernoulli's equation will reduce to;
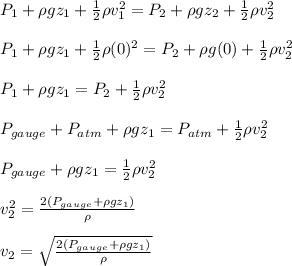
where;
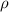 is the density of seawater = 1030 kg/m³
is the density of seawater = 1030 kg/m³
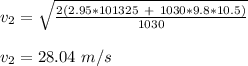
Therefore, the water is flowing at the rate of 28.04 m/s.