Answer: 0.029 V
Step-by-step explanation:
For the given chemical reaction :
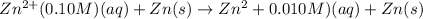
Using Nernst equation :
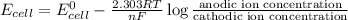
where,
F = Faraday constant = 96500 C
R = gas constant = 8.314 J/mol.K
T = room temperature = 298 K
n = number of electrons in oxidation-reduction reaction = 2
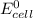 = standard electrode potential of the cell = 0 (as both metals are same )
= standard electrode potential of the cell = 0 (as both metals are same )
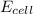 = emf of the cell = ?
= emf of the cell = ?
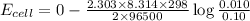
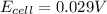
Thus the cell potential will be 0.029 V