Answer:
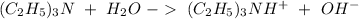
Step-by-step explanation:
For this question, we have to remember that definition of acid and base in the Bronsted-Lowry theory:
Acid
A substance with the ability to produce a hydronium ion (
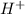 ).
).
Base
A substance with the ability to accepts a hydronium ion (
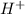 ).
).
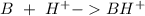
If we check the reaction mechanism (figure 1). We can see that the lone pair of electrons in the "N" atom will remove an "H" from the water molecule producing a positive charge in the nitrogen and a hydroxyl group (
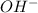 ).
).
With all this in mind, the net ionic equation would be:
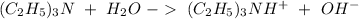
I hope it helps!