Answer:
the voltage drop across this same diode will be 760 mV
Step-by-step explanation:
Given that:
Temperature T = 300°K
current
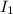 = 100 μA
= 100 μA
current
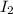 = 1 mA
= 1 mA
forward voltage
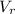 = 700 mV = 0.7 V
= 700 mV = 0.7 V
To objective is to find the voltage drop across this same diode if the bias current is increased to 1mA.
Using the formula:
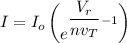
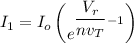
where;
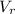 = 0.7
= 0.7
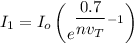
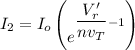
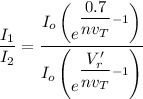
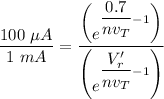
Suppose n = 1
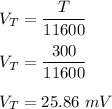
Then;
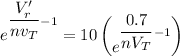
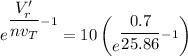
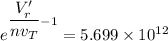
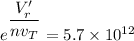
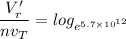
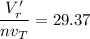
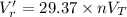
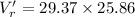
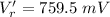
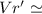 760 mV
760 mV
Thus, the voltage drop across this same diode will be 760 mV