Answer:
9.82 ×
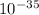 Hz
Hz
Step-by-step explanation:
De Broglie equation is used to determine the wavelength of a particle (e.g electron) in motion. It is given as:
λ =
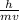
where: λ is the required wavelength of the moving electron, h is the Planck's constant, m is the mass of the particle, v is its speed.
Given that: h = 6.63 ×
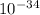 Js, m = 2.50 kg, v = 2.70 m/s, the wavelength, λ, can be determined as follows;
Js, m = 2.50 kg, v = 2.70 m/s, the wavelength, λ, can be determined as follows;
λ =
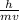
=
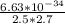
=
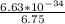
= 9.8222 ×
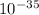
The wavelength of the object is 9.82 ×
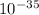 Hz.
Hz.