Answer:
2 m/s
Step-by-step explanation:
The electromagnetic flow-metre work on the principle of electromagnetic induction. The induced voltage is given as
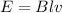
where
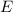 is the induced voltage = 2.88 mV = 2.88 x 10^-3 V
is the induced voltage = 2.88 mV = 2.88 x 10^-3 V
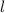 is the distance between the electrodes in this field which is equivalent to the diameter of the tube = 1.2 cm = 1.2 x 10^-2 m
is the distance between the electrodes in this field which is equivalent to the diameter of the tube = 1.2 cm = 1.2 x 10^-2 m
 is the velocity of the fluid through the field = ?
is the velocity of the fluid through the field = ?
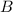 is the magnetic field = 0.120 T
is the magnetic field = 0.120 T
substituting, we have
2.88 x 10^-3 = 0.120 x 1.2 x 10^-2 x

2.88 x 10^-3 = 1.44 x 10^-3 x

 = 2.88/1.44 = 2 m/s
= 2.88/1.44 = 2 m/s