Answer:
24
Step-by-step explanation:
The mass = 3 kg
at point O all the mechanical energy of the system is due to its potential energy PE. The body is at rest.
PE = mgh
but ME = PE + KE = constant (law of energy conservation)
KE is the kinetic energy
since KE is zero at this point, then,
ME = mgh
where m is the mass
g is acceleration due to gravity = 9.81 m/s^2
h is the height = O
ME = 3 x 9.81 x O
ME = 29.43-O
At point A the total ME is due to its PE and its kE
PE at this point = mgh = 3 x 9.81 x A = 29.43-A
KE =
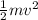
velocity = v at this point, therefore,
KE =
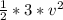 =
=
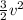
therefore,
ME = 29.43-A +
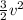
Equating ME for the points O and A, we have
29.43-O = 29.43-A +
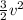
29.43-O - 29.43-A =
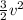
(O - A)29.43 =
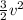
O - A = 0.051
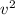 this is the distance between point O and A
this is the distance between point O and A
For point B
PE = 29.43-B
KE =
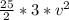 = 37.5
= 37.5
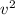 (velocity is equal to
(velocity is equal to
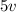 at this point)
at this point)
therefore,
ME = 29.43-B + 37.5
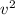
Equating the ME for points A and B, we have
29.43-A +
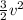 = 29.43-B + 37.5
= 29.43-B + 37.5
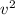
29.43-A - 29.43-B = 37.5
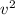 -
-
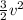
(A - B)29.43 = 36
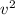
A - B = 1.22
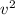 this is the distance between points A and B
this is the distance between points A and B
The distance between points A & B divided by the distance between points 0 & A will be
1.22
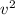 /0.051 = 23.9 ≅ 24
/0.051 = 23.9 ≅ 24