Complete Question
The complete question is shown on the first uploaded image
Answer:
Yes the test suggest that the true average percentage of organic matter in such soil is something other than 3%
Explanation:
From the question we are told that
The sample mean is
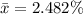
The standard deviation is
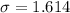
The standard error is
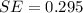
The sample size is

The level of significance is
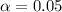
The null hypothesis is
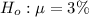
The alternative hypothesis is
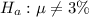
Now the degree of freedom is evaluated as
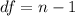
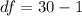
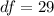
The test statistics is mathematically evaluated as
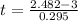
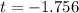
The p-value is obtained from the the student t -distribution table , the value is
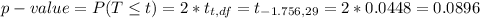
The reason for the 2 in the equation is because the test is a two -tailed test i.e -1.756 and 1.756
Given that the
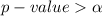 then we fail to reject the null hypothesis
then we fail to reject the null hypothesis
Hence the test the suggest that the true average percentage of organic matter in such soil is something other than 3%