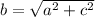Answer:
It is reduced to the equation of the Theorem of Pythagoras.
Explanation:
Any triangle can be modelled by this formula under the Law of Cosine:
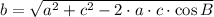
Where:
 ,
,
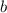 ,
,
 - Side lengths, dimensionless.
- Side lengths, dimensionless.
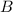 - Angle opposed to the side
- Angle opposed to the side
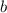 , measured in sexagesimal degrees.
, measured in sexagesimal degrees.
Now, let suppose that angle B is a right angle (90º), so that b is a hypotenuse and a and c are legs. Hence:
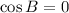
And the equation is reduced to the form of the Theorem of Pythagoras, that is to say: