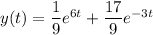(a) Expand the given expression as
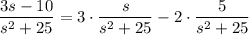
You should recognize the Laplace transform of sine and cosine:
![L[\cos(at)]=\frac s{s^2+a^2}](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/5ybm530p7xvbvlklzoij19ct9a9354odhm.png)
![L[\sin(at)]=\frac a{s^2+a^2}](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/1sbjlel6u2gozxft2gdy2auw5bq5n187ji.png)
So we have
![L^(-1)\left[(3s-10)/(s^2+25)\right]=3\cos(5t)-2\sin(5t)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/spe9rt7334qxykw7l0j0ezgx7wxzsnpefa.png)
(b) Take the Laplace transform of both sides:
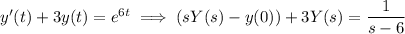
Solve for
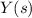 :
:
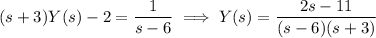
Decompose the right side into partial fractions:
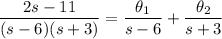
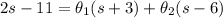
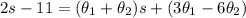
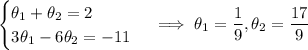
So we have
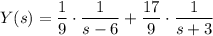
and taking the inverse transforms of both sides gives