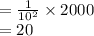Answer:
At 3 meter distance, the per-second count is 222.22 and at a 10 meter distance, the per-second count is 20.
Step-by-step explanation:
The number of particles (N) counts are inversely proportional to the distance between the source and the detector.
By using the below formula we can find the number of counts.
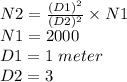
The number of count per second, when the distance is 3 meters.
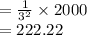
Number of count per second when the distance is 10 meters.