Answer:
6.79 atm
Step-by-step explanation:
Applying Dalton's law of partial pressure:
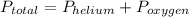 , where
, where
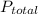 = total partial pressure of all the component gases in the mixture,
= total partial pressure of all the component gases in the mixture,
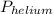 = partial pressure of helium gas, and
= partial pressure of helium gas, and
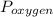 = partial pressure of oxygen gas.
= partial pressure of oxygen gas.
From the illustration,
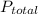 = 7.00 atm and
= 7.00 atm and
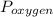 = 0.21 atm. Hence, the partial pressure due to helium is calculated such that:
= 0.21 atm. Hence, the partial pressure due to helium is calculated such that:
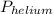 =
=
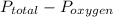
= 7.00 - 0.21
= 6.79 atm
Therefore, the partial pressure due to helium in order to maintain the pressure due to oxygen at 0.21 atm would be 6.79 atm.