Answer:
Product: ethyl L-valinate
Step-by-step explanation:
If we want to understand what it is the molecule produced we have to analyze the reagents. We have valine an amino acid, in this kind of compounds we have an amine group (
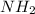 ) and a carboxylic acid group (
) and a carboxylic acid group (
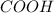 ). Additionally, we have an alcohol (
). Additionally, we have an alcohol (
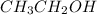 ) in the presence of HCl (a strong acid) in the first step, and a base (
) in the presence of HCl (a strong acid) in the first step, and a base (
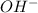 ).
).
When we have an acid and an alcohol in a vessel we will have an esterification reaction. In other words, an ester is produced. As the first step, the oxygen in the C=O (in the carboxylic acid group) would be protonated. In the second step, the ethanol attacks the carbon in the C=O of the carboxylic acid group producing a new bond between the oxygen in the ethanol and the carbon in the carboxylic acid. In step 3, a proton is transferred to produce a better leaving group (
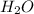 ). In step 4, a water molecule leaves the main structure to produce again the double bond C=O. Finally, a base (
). In step 4, a water molecule leaves the main structure to produce again the double bond C=O. Finally, a base (
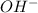 ) removes the hydrogen from the C=O bond to produce ethyl L-valinate
) removes the hydrogen from the C=O bond to produce ethyl L-valinate
See figure 1
I hope it helps!