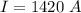Answer:
The current is
Step-by-step explanation:
From the question we are told that
The diameter of the wire is
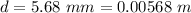
The magnetic field is
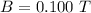
Generally the radius of the wire is mathematically evaluated as
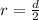
substituting values
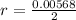
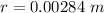
Generally the magnetic field is mathematically represented as
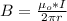
=>
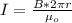
Here
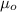 is the permeability of free space with value
is the permeability of free space with value
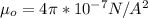
substituting values
=>
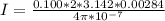
=>