Complete Question
In a genetics experiment on peas, one sample of offspring contained 372 green peas and 35 yellow peas. Based on those results, estimate the probability of getting an offspring pea that is green. Is the result reasonably close to the value of 3/4 that was expected?
Answer:
The probability is
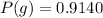
No it is not close to the probability expected
Explanation:
From the question we are told that
The sample size is
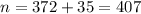
The number of green peas is
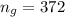
The number of yellow peas is
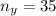
The probability of getting an offspring pea that is green is mathematically represented as
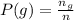
substituting values
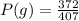
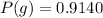
The expected probability is
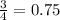
But what we got is
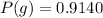
So we can say that the value obtained is not equal to the expected value