Answer:
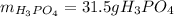
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello,
In this case, the undergoing chemical reaction is:
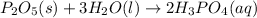
Thus, since the diphosphorus pentoxide to water molar ratio is 1:3 and we are given the mass of both of them, for the calculation of the maximum mass phosphoric acid that is yielded, one could first identify the limiting reactant, for which we compute the available moles of diphosphorus pentoxide (molar mass 142 g/mol):
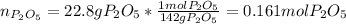
And the moles of diphosphorus pentoxide that are consumed by 13.5 g of water (molar mass 18 g/mol):
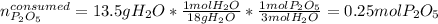
Hence, since less moles of diphosphorus pentoxide are available, we sum up it is the limiting reactant, therefore, the maximum mass of phosphoric acid (molar mass 98 g/mol) is computed by considering the 1:2 molar ratio between them as follows:
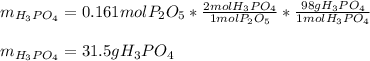
Regards.