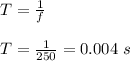Answer:
The answer is below
Step-by-step explanation:
An AC voltage is represented by the relation v= 12 sin(500πt). Determine the:
The equation of an AC voltage is given as:
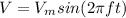
Where Vm is the maximum value of voltage and f is the frequency
From V= 12 sin(500πt), Vm = 12, 2πft = 500πt
(a) The peak to peak voltage is total amplitude (both the negative and positive amplitude) of the voltage, it is the difference between the positive amplitude and the negative amplitude. The peak to peak voltage (
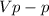 ) is given as:
) is given as:
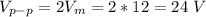
b) The frequency is the number of oscillation per second. The frequency (f) is gotten from:
2πft = 500πt
2f = 500
f = 500/2
f = 250 Hz
c) The root mean square voltage is the dc value of the voltage. It is given by:
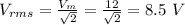
d) The period (T) is the time taken to complete one oscillation, it is given by: