Answer:
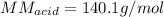
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello,
In this case, since the acid is monoprotic, we can notice a 1:1 molar ratio between, therefore, for the titration at the equivalence point, we have:
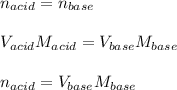
Thus, solving for the moles of the acid, we obtain:
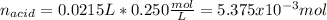
Then, by using the mass of the acid, we compute its molar mass:
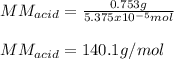
Regards.