Answer:
Explanation:
Let the equation of a polynomial is,
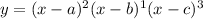
Zeroes of this polynomial are x = a, b and c.
For the root x = a, multiplicity of the root 'a' is 2 [given as the power of (x - a)]
Similarly, multiplicity of the roots b and c are 1 and 3.
Effect of multiplicity on the graph,
If the multiplicity of a root is even then the graph will touch the x-axis and if it is odd, graph will cross the x-axis.
Therefore, graph will cross x -axis at x = b and c while it will touch the x-axis for x = a.
In this question,
The given polynomial is,
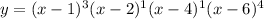
Degree of the polynomial = 3 + 1 + 1 + 4 = 9
The graph of the function will cross through the x-axis at x = 1, 2, 4 only, The graph will touch to the x-axis at 6 only.
At the zero of 2 , the graph of the function will CROSS the x-axis.