Answer:
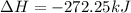 for 1 mole of NO.
for 1 mole of NO.
Step-by-step explanation: Hess' Law of Constant Summation or Hess' Law states that the total enthalpy change of a reaction with multiple stages is the sum of the enthalpies of all the changes.
For this question:
1)
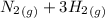 =>
=>
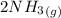
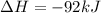
2)
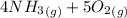 =>
=>
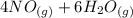

Amonia (
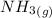 ) appeares as product in the first equation and as reagent in the 2 reaction, so when adding both, there is no need to inverse reactions. However, in the 2nd, there are 4 moles of that molecule, so to cancel it, you have to multiply by 2 the first chemical equation and enthalpy:
) appeares as product in the first equation and as reagent in the 2 reaction, so when adding both, there is no need to inverse reactions. However, in the 2nd, there are 4 moles of that molecule, so to cancel it, you have to multiply by 2 the first chemical equation and enthalpy:
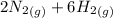 =>
=>
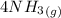

Now, adding them:
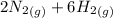 =>
=>
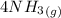

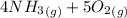 =>
=>
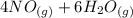

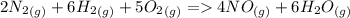
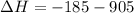
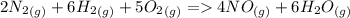
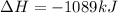
Note net enthalpy is for the formation of 4 moles of nitric oxide.
For 1 mole:
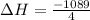
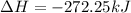
To form 1 mol of nitric oxide from nitrogen, oxygen and hydrogen, net change in enthalpy is
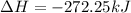 .
.