Answer:
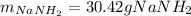
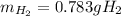
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello,
In this case, the reaction between sodium and ammonia is:
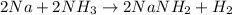
Thus, as we know the initial masses of both sodium and ammonia, we should first identify the limiting reactant, for which we firstly compute the available moles of sodium:
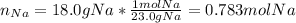
And the moles of sodium consumed by 21.4 g of ammonia (2:2 mole ratio):
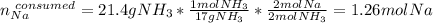
In such a way, since less moles of sodium are available than consumed by ammonia, we can say, sodium is the limiting reactant. Furthermore, the mass of both sodium amide (39 g/mol) and hydrogen gas (2 g/mol) that are produced turn out:
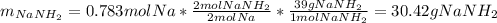
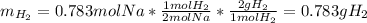
Best regards.