Answer: The calculated molar enthalpy change of reaction for his second trial was -108 kJ.
Explanation:-
Molarity of a solution is defined as the number of moles of solute dissolved per Liter of the solution.

Thus

Thus


Given for second trial:


0.05 moles of
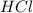 reacts with 0.05 moles of
reacts with 0.05 moles of
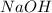 to release heat = 54 kJ
to release heat = 54 kJ
0.1 moles of
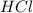 reacts with 0.05 moles of
reacts with 0.05 moles of
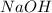 to release heat =
to release heat =

Thus calculated molar enthalpy change of reaction for his second trial was -108 kJ.