Answer:
The P-value is the probability of getting a test statistic at least as extreme as the one representing the sample data, assuming that the null hypothesis is true.
Explanation:
The P-value is the probability of getting a test statistic at least as extreme as the one representing the sample data, assuming that the null hypothesis is true.
The p-value is the probability that, if the null hypothesis were true,sampling variation would yield and estimate that is further away from the hypothesised value than our data estimate. The p-value shows us how possible it is to get a result like this if the null hypothesis is true.
Assuming we have a null hypothesis and an alternative hypothesis computed as follows.
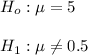
If P-value is less than or equal to
 , we will reject the null hypothesis.
, we will reject the null hypothesis.