Answer: f(x) will have vertical asymptotes at x=-2 and x=2 and horizontal asymptote at y=3.
Explanation:
Given function:
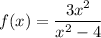
The vertical asymptote occurs for those values of x which make function indeterminate or denominator 0.
i.e.
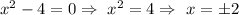
Hence, f(x) will have vertical asymptotes at x=-2 and x=2.
To find the horizontal asymptote , we can see that the degree of numerator and denominator is same i.e. 2.
So, the graph will horizontal asymptote at
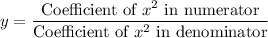
i.e.
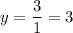
Hence, f(x) will have horizontal asymptote at y=3.