Answer:
Explanation:
Given that:
A simple random sample n = 28
sample standard deviation S = 12.65
standard deviation
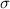 = 11.53
= 11.53
Level of significance ∝ = 0.05
The objective is to test the claim that the number of pieces in a set has a standard deviation different from 11.53.
The null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis can be computed as follows:
Null hypothesis:
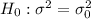
Alternative hypothesis:
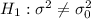
The test statistics can be determined by using the following formula in order to test if the claim is statistically significant or not.
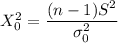
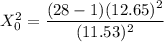
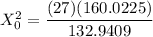
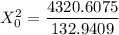
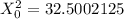
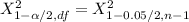
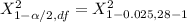
From the chi-square probabilities table at 0.975 and degree of freedom 27;
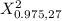 = 14.573
= 14.573
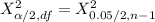
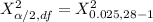
From the chi-square probabilities table at 0.975 and degree of freedom 27;
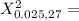 43.195
43.195
Decision Rule: To reject the null hypothesis if
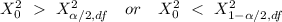 ; otherwise , do not reject the null hypothesis:
; otherwise , do not reject the null hypothesis:
The rejection region is
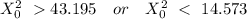
Conclusion:
We fail to reject the null hypothesis since test statistic value 32.5002125 lies between 14.573 and 43.195.