a. I've attached a plot of the surface. Each face is parameterized by
•
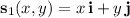 with
with
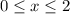 and
and
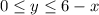 ;
;
•
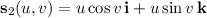 with
with
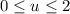 and
and
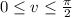 ;
;
•
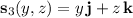 with
with
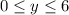 and
and
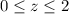 ;
;
•
 with
with
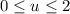 and
and
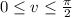 ; and
; and
•
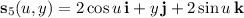 with
with
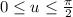 and
and
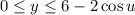 .
.
b. Assuming you want outward flux, first compute the outward-facing normal vectors for each face.
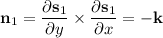
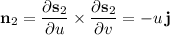
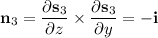
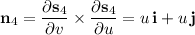
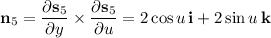
Then integrate the dot product of f with each normal vector over the corresponding face.
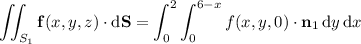
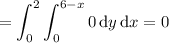
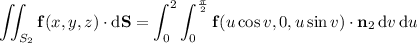
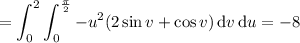
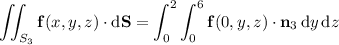
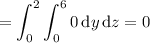
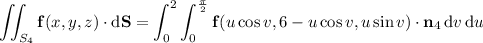
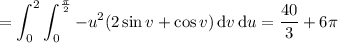
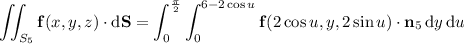
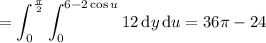
c. You can get the total flux by summing all the fluxes found in part b; you end up with 42π - 56/3.
Alternatively, since S is closed, we can find the total flux by applying the divergence theorem.
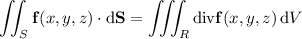
where R is the interior of S. We have
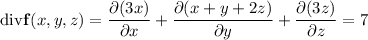
The integral is easily computed in cylindrical coordinates:
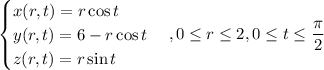
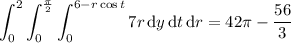
as expected.