Answer:
10.75 A
The current is in opposite direction since it causes a repulsion force between the wires
Step-by-step explanation:
Force per unit length on the wires = 4.30×10^−5 N/m
distance between wires = 2.6 cm = 0.026 m
current through one wire = 0.52 A
current on the other wire = ?
Recall that the force per unit length of two wires conducting and lying parallel and close to each other is given as
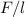 =
=
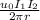
where
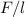 is the force per unit length on the wires
is the force per unit length on the wires
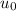 = permeability of vacuum = 4π × 10^−7 T-m/A
= permeability of vacuum = 4π × 10^−7 T-m/A
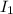 = current on the first wire = 0.520 A
= current on the first wire = 0.520 A
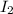 = current on the other wire = ?
= current on the other wire = ?
r = the distance between the two wire = 0.026 m
substituting the value into the equation, we have
4.30×10^−5 =
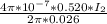 =
=
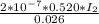
4.30×10^−5 = 4 x 10^-6
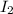
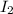 = (4.30×10^-5)/(4 x 10^-6) = 10.75 A
= (4.30×10^-5)/(4 x 10^-6) = 10.75 A
The current is in opposite direction since it causes a repulsion force between the wires.