Answer:
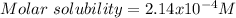
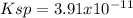
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello,
In this case, given that 0.0167 grams of calcium fluoride in 1 L of solution form a saturated one, we can notice it is the solubility, therefore, the molar solubility is computed by using the molar mass of calcium fluoride (78.1 g/mol):
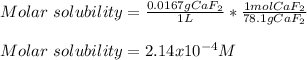
Next, since dissociation equation for calcium fluoride is:
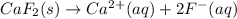
The equilibrium expression is:
![Ksp=[Ca^(2+)][F^-]^2](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/zzmc07yep1karrfpe89mfohuprmzyybi82.png)
We can compute the solubility product by remembering that the concentration of both calcium and fluoride ions equals the molar solubility, thereby:
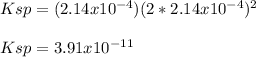
Regards.