Answer:
For sample size n = 39 ; P(X < 31.6) = 0.9756
For sample size n = 76 ; P(X < 31.6) = 0.9970
Explanation:
Given that:
population mean μ = 31
standard deviation σ = 1.9
sample mean
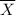 = 31.6
= 31.6
Sample size n Probability
39
76
The probabilities that the sample mean is less than 31.6 for both sample size can be computed as follows:
For sample size n = 39
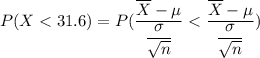
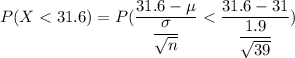
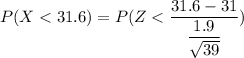
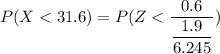
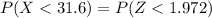
From standard normal tables
P(X < 31.6) = 0.9756
For sample size n = 76
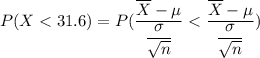
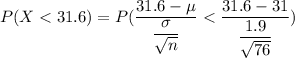
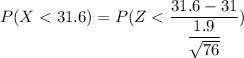
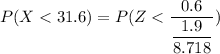
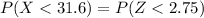
From standard normal tables
P(X < 31.6) = 0.9970