Answer:
The solution(s) are in order with respect to the attachments
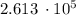 Joules ; 5. Adding the same amount of heat to two different objects will produce the same increase in temperature ; 2. Same speed in both ; 2. A
Joules ; 5. Adding the same amount of heat to two different objects will produce the same increase in temperature ; 2. Same speed in both ; 2. A
Step-by-step explanation:
Diagram 1 ( Liquid Nitrogen ) : So as you can see, we want our units in Joules here, and can therefore multiply the mass of gaseous nitrogen and the latent heat of liquid nitrogen, to cancel the units kg, and receive our solution - in terms of Joules. Let's do it.
q ( energy removed ) = mass of nitrogen
 latent heat of liquid nitrogen,
latent heat of liquid nitrogen,
q = 1.3 kg
 2.01
2.01
 10⁵ J / kg =
10⁵ J / kg =
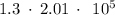 =
=
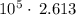 =
=
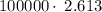 =
=
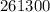 Joules =
Joules =
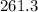 kiloJoules = 2.613
kiloJoules = 2.613
 10⁵Joules is the energy that must be removed
10⁵Joules is the energy that must be removed
Diagram 2 : The same amount of heat does not necessarily mean the same increase in temperature for two different objects. The increase in temperature depends on the specific heat capacity of the substance. Therefore your solution is 5 ) Adding the same amount of heat to two different objects will produce the same increase in temperature.
Diagram 3 : The temperatures in both glasses are the same, and hence the molecules have the same average speed. Therefore your solution is 2 ) Same speed in both.
Diagram 4 : Glass A has more water molecules, and hence has more thermal energy. Your solution is 2 ) A.