Answer:
Rate constants are temperature dependent.
Step-by-step explanation:
Reaction rate is used to quantify the rate of chemical reaction. There is a relationship between the reaction rate and the half-life of the reaction and the Gibbs free energy of activation, and the reaction rate is temperature dependent according to the equation.
For a reaction shown below
a A + b B ⇒ c C
The rate of reaction of the reaction is given by
![r = k(T) [A]^(m)[B]^(n)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/zgm9xjzhu6k200n4ldxbr7dz4kwb3qzfw7.png)
where k(T) is the reaction constant, which is seen to be dependent on the temperature of the reaction.
Also, k(T) is numerically equal to
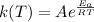
where
r = reaction rate
A = pre exponential factor
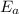 = Activation energy
= Activation energy
R = gas constant
T = temperature
and m and n are experimentally determined partial orders in [A] and [B]