Answer:
If the value of our test statistics is less than the critical value of t at 7 degrees of freedom at a 10% level of significance for the right-tailed test (which is 1.415), then we have insufficient evidence to reject our null hypothesis as it will not fall in the rejection region.
If the value of our test statistics is more than the critical value of t at 7 degrees of freedom at a 10% level of significance for the right-tailed test (which is 1.415), then we have sufficient evidence to reject our null hypothesis as it will fall in the rejection region.
Explanation:
We are given that the means of two populations using paired observations. Suppose that
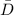 = 3.125,
= 3.125,
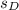 = 2.911, and n = 8, and that you wish to test the hypothesis below at the 10% level of significance.
= 2.911, and n = 8, and that you wish to test the hypothesis below at the 10% level of significance.
Let D = difference between the two paired observations.
So, Null Hypothesis,
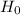 :
:
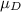 = 0
= 0
Alternate Hypothesis,
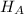 :
:
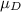 > 0
> 0
The test statistics that would be used here is Paired t-test for dependent samples;
T.S. =
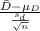 ~
~
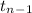
where,
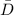 = 3.125,
= 3.125,
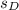 = 2.911, and n = 8
= 2.911, and n = 8
The decision rule for rejecting the null hypothesis in the given hypothesis test would be;
- If the value of our test statistics is less than the critical value of t at 7 degrees of freedom at a 10% level of significance for the right-tailed test (which is 1.415), then we have insufficient evidence to reject our null hypothesis as it will not fall in the rejection region.
- If the value of our test statistics is more than the critical value of t at 7 degrees of freedom at a 10% level of significance for the right-tailed test (which is 1.415), then we have sufficient evidence to reject our null hypothesis as it will fall in the rejection region.